Maintenance has long been the backbone of operational reliability. Whether in manufacturing plants, commercial buildings, or public infrastructure, the importance of timely and effective maintenance cannot be overstated.
Traditionally, maintenance relied heavily on either scheduled checks or reactive fixes, both of which had significant cost implications and posed risks of unplanned downtime. However, with the rise of technologies like IoT (Internet of Things), a smarter, more strategic approach has emerged: predictive maintenance.
What is predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a data-driven approach to anticipate equipment failures before they happen. Instead of sticking to fixed schedules or waiting for breakdowns, this method uses real-time monitoring and advanced analytics to assess the condition of assets. When early signs of wear or anomalies are detected, maintenance actions are taken just in time, not too early or too late.
The concept of predictive maintenance solutions has its roots in the aviation and manufacturing sectors, where equipment failure could result in catastrophic losses. Over the past two decades, as sensors, connectivity, and data became more accessible, the strategy evolved into a mature field, expanding into tailored predictive maintenance programs used in modern industries.
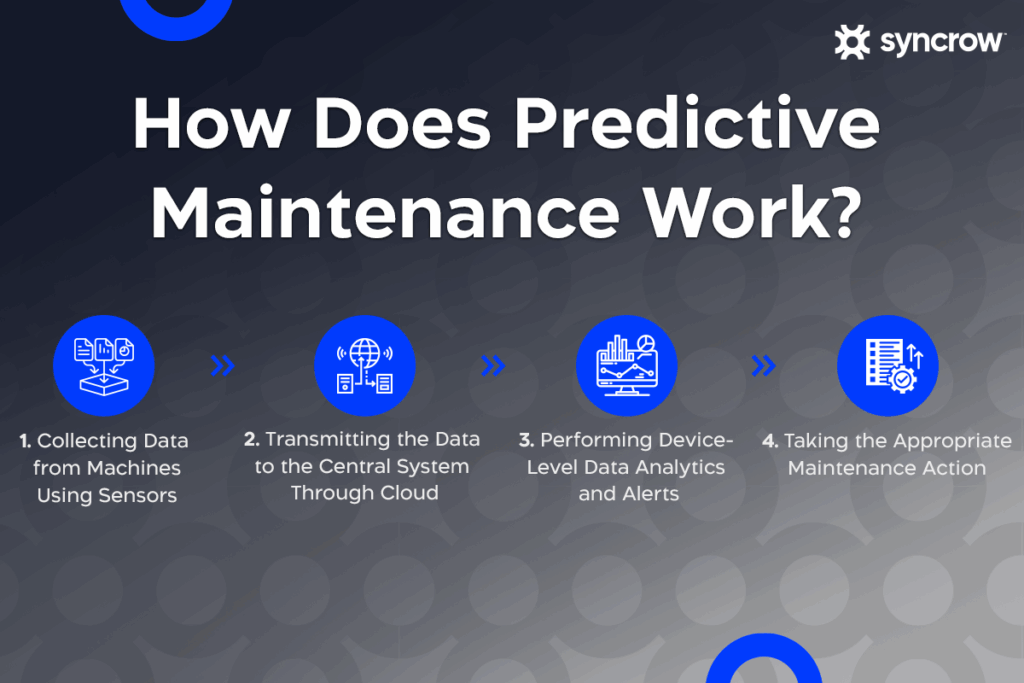
How does predictive maintenance work?
Predictive maintenance technologies work by collecting real-time data from equipment, analyzing that data, and generating actionable insights. This continuous stream of information comes from various IoT sensors and systems, which are then processed using predictive analytics to forecast potential points of failure.
Maintenance teams get notified to intervene only when necessary, maximizing equipment uptime and reducing unnecessary maintenance costs.
Technologies used in predictive maintenance
Sensors
Sensors are the frontline tools in predictive maintenance. They include sensors to measure vibration, infrared, sound, fluid leaks, and many others. Together, they help capture the subtle signs of wear and tear that precede equipment failure.
IoT Gateways
IoT gateways bridge the gap between sensors in the field and the central platform. They collect data locally and often perform initial preprocessing before sending it to the cloud. These gateways ensure seamless communication, especially in environments where different types of equipment and protocols coexist.
IoT Platform
An IoT platform acts as the brain of the predictive maintenance system. It aggregates data from various sources, enables integration across assets, and allows staff to manage workflows, notifications, and thresholds. This software serves as the central hub for connectivity, visualization, and real-time decision-making.
Cloud Technology
Cloud computing plays a crucial role in scaling predictive maintenance systems. It allows vast amounts of data to be stored, accessed, and processed without the limitations of on-premise infrastructure. It also supports remote monitoring, which enables distributed teams to maintain oversight across multiple sites.
Data Analytics
Raw sensor data is only as good as the insights derived from it. And this is where data analytics comes in. By identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies, data tools empower maintenance professionals to make informed decisions quickly.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence enhances the accuracy and scope of predictive maintenance. From advanced fault detection algorithms to machine learning and predictive models that improve with every new data point, AI automates complex diagnostics and enables systems to evolve over time.
Types of predictive maintenance
Different types of predictive maintenance strategies are used based on the kind of equipment and operating environment:
- Thermal Imaging: Detects heat signatures to identify overheating components like motors and electrical systems.
- Sound Analysis: Picks up acoustic signals that suggest friction, looseness, or structural issues.
- Vibration Analysis: Monitors mechanical movement to catch misalignment, imbalance, or degradation in rotating equipment.
- Ultrasonic Analysis: Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect leaks or internal component flaws not visible externally.
- Current and Voltage Sensors: Tracks electrical parameters to identify changes in power consumption or abnormalities in electrical systems.
Predictive Maintenance vs Preventive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance are both proactive strategies and are considered computerized maintenance management, but they differ significantly in approach, technology, and efficiency. Understanding their key differences can help organizations choose the right strategy for their operations.
Here’s the main difference between predictive maintenance and preventive maintenance:
| Feature | Predictive Maintenance | Preventive Maintenance |
| Basis | Real-time condition monitoring | Time-based or usage-based scheduling |
| Timing | Maintenance is performed when data indicates it’s needed | Maintenance is performed at regular intervals |
| Efficiency | Highly efficient and avoids both under- and over-maintenance | Risk of unnecessary servicing or missed failures |
| Cost | Higher initial setup, lower long-term costs | Lower initial setup, possibly higher long-term costs |
| Technology | Relies on sensors, IoT, and analytics | Typically uses logs and routine checks |
| Downtime Risk | Minimal due to early issue detection | Potential downtime if failure occurs between intervals |
| Data Dependency | Depends on live operational and historical data | Minimal data usage |
| Workforce Utilization | Maintenance team focuses only on actual issues | Team follows routine schedules regardless of need |
Use Cases of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance was first widely adopted in manufacturing, particularly in industries with high capital equipment like automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery. These environments rely on complex systems where equipment failure can halt entire production lines.
With the rise of IoT, predictive maintenance has expanded into sectors such as facility management for commercial buildings. HVAC systems, elevators, lighting networks, and water systems can now be monitored in real-time.
The integration of smart sensors and cloud platforms allows building operators to manage scheduled maintenance more intelligently. This is especially relevant for modern smart buildings, where ensuring optimal operational efficiency is key to both cost savings and tenant satisfaction.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Implementing predictive maintenance offers several measurable benefits:
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: By servicing only when needed, businesses can eliminate unnecessary labor and part replacements.
- Increased Equipment Lifespan: Early detection of issues helps preserve the integrity of critical components.
- Minimized Downtime: Continuous monitoring means fewer unexpected breakdowns.
- Improved Safety: Identifying faults before they become hazards protects staff and infrastructure.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Maintenance teams can focus on actual needs rather than routine checklists.
According to a 2022 report from Deloitte, predictive maintenance can reduce downtime by up to 15%, increase labor productivity by up to 20%, and save up to 5% in new equipment costs.
Challenges of implementing predictive maintenance technologies
Despite its advantages, rolling out a predictive maintenance strategy comes with challenges:
- High Initial Investment: Setting up sensors, gateways, and platforms can be capital-intensive.
- Data Overload: Managing and interpreting large volumes of data requires robust analytics capabilities.
- Skill Gaps: Teams may need training in interpreting sensor data and using predictive tools.
- Integration Issues: Legacy systems may not easily connect to modern predictive platforms.
- False Positives: Early-stage systems may generate alerts for non-critical issues, leading to confusion or mistrust.
Final thoughts
Predictive maintenance is transforming the way organizations approach asset management. With the right combination of sensors, platforms, and analytics, companies can shift from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies, saving money, enhancing reliability, and creating more sustainable operations.
While challenges exist, the long-term value makes it a compelling investment for any forward-thinking organization. If you’re looking to make your building smarter and more efficient in the long term, you can get a free consultation by contacting the Syncrow team.





